Requirements for the optics
- Minimal adjustment of the working distance (WD): Lateral chromatic aberration should be kept to a minimum to ensure sharp and accurate images.
- Chromatic correction/optimization: The optical design have to be tuned to the spectral range of the application. Specific characteristics are more important than widest possible bandwidth coverage.
- Consistent level of light transmission: The light transmission of the lens must not decrease too much, especially at wavelengths above 1400 nm.
- Specific adjustments: These include primary magnification (PMAG), working distance (WD), space limitations and depth of field (DoF). This requirements apply to telecentric optics but are equally valid for entocentric and epicentric optics.
Requirements for the lighting
As in any image processing application the correct lighting is crutial for spectral imaging:
- Size and alignment of the lighting: the lighting have to meet the right alignment, whether diffuse or directed.
- Spectral range: The specific applikation is defining the choice of narrow- or broadband lighting.
- Intensity: High intensity is required for reflective applications, while lower intensity is necessary for transmitting light applications.
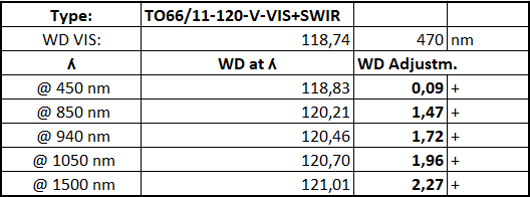
vicotar® TO66/11-VSWIR for 2/3 Inch sensors
Apochromatic correction was used for the BLUE Vision TO66/11 lens in order to optimize the optics for the VIS to SWIR range. The low adjustment of the working distance (WD) and the diffraction MTF at aperture F14 underline the high precision of this optic.
vicolux® lighting solutions for VNIR, NIR and SWIR applications
vicolux® high-performance LED lighting offers customized lighting solutions for different spectral ranges:
- Narrow-band LEDs for SWIR: These offer sufficient power and are ideal for specific applications.
- Broadband LEDs for VIS and NIR: These are also powerful and offer a wide range of applications.
- Combination of narrowband wavelengths: These are put together as an array for specific requirements.
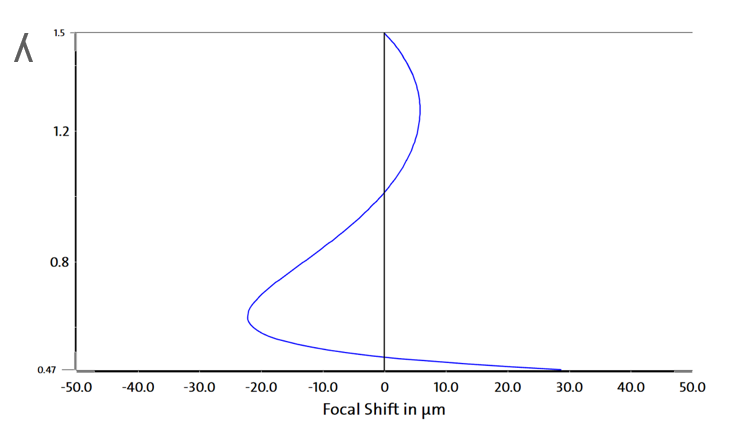
Lenses have different focal lengths at different wavelengths -> lateral chromatic aberration Δf
The Abbe number ν (nue) is a measure of the chromatic dispersion of glass
Δf is inversely proportional to the Abbe number ν
The aim of apochromatic correction is to use this relationship by systematically combining different types of glass to correct 3 different wavelengths; e.g. combination of short flint (KzF) glass.